What is Hyper threading? How does it Work? Any Drawbacks?
The number of cores has increased in processors over the past few years, but is hyperthreading among the most important additions yet?
Hyperthreading is a technology that has been gaining popularity in the past several years. Intel has been using it more and more in its high-end chips to provide better improvement in gaming.
So what is hyper threading, and should you get a CPU with hyperthreading, or does it have any drawbacks?
In this article, I’ll explain everything you need to know about hyperthreading and how it can benefit your computer performance.
Content Index hide
Role of CPU and Cores
The CPU is like the brain of your computer. It processes the information provided by other computer parts and generates output data or performs actions accordingly. Whenever you start a program, the processor interprets the instructions and displays the result.
Then, you might have heard about “cores” in CPUs, and each core is like an additional CPU that can execute one process at a time. Older processors had only one core, but with the advancements, today’s processors have quad or even eight cores, which means they can perform multiple tasks at the same time.
So, it’s true, the more cores, the better, but what about hyper threading? Let’s know.
What is Hyper Threading in CPU?
Traditional processors have only one thread (single-threaded), so they can only perform one function at a time. Hyperthreading, on the other hand, is the Intel version of simultaneous multithreading (SMT).
SMT divides each CPU core into two virtual cores, allowing two sets of instructions to be processed simultaneously (as long as the program supports it). This means multithreading effectively doubles the number of cores available to the CPU.
Therefore, if you have a four-core processor with hyperthreading, you will have eight virtual cores . This is different from having double the number of physical cores.

Hyperthreading helps increase CPU productivity by allowing it to process twice the number of processes simultaneously; thus, the CPU can easily handle more demanding applications with ease.
How does hyperthreading work?
Hyperthreading uses virtual kernels, also known as logical cores, to share resources such as runtime and cache. This differs from having separate physical CPU cores. Hyperthreading is the increased efficiency of each core as resources are shared between logical cores. When one logical core is idle, another can use the resources to complete its tasks.
It is important to note that virtual kernels/cores do not have the same computing power as physical cores . Therefore, having more physical cores is always preferable to having more virtual ones, as each physical core has a unique architecture that makes it more efficient and powerful.
While hyperthreading can improve the performance of a quad-core processor, an eight-core processor will still outperform both a four-core with hyperthreading and a standard quad-core processor.
The effectiveness of hyperthreading depends on the software or program being used. If the software doesn’t create multiple streams or isn’t compatible with this hyperthreading technology, then the efficiency of the processing cores will be lower.
The Drawbacks of Hyper threading
Now you got what is hyper threading, following are the drawbacks comes with it:
- A CPU with hyperthreading consumes more energy than a CPU without it. This additional energy consumption may be unnecessary if you do not use hyperthreading. Work of multithreading, be it hyper-threading from Intel and SMT from AMD, accompanied by increased heat output too that can cause thermal throttling.
- Any software working you should be optimized for multithreading, otherwise, at best, there will be no increase in productivity, and at worst, the application will work incorrectly.
- Additionally, processors with hyperthreading tend to be some expensive. Hence, if hyperthreading is unnecessary for your requirements, it may not be worth investing extra money.
Hyperthreading technology: Intel vs AMD
The Pentium 4, an Intel processor with the innovative NetBurst architecture, was released in November 2002. One of its many innovations was the hyper-threading technology. If I talk about AMD, they introduced their multithreading SMT technology along with their Ryzen line of processors in 2017. This technology operates similarly to hyper-threading and has the same features described above.
Is it Worth Getting CPU with Hyper Threading?
First, it is important to prioritize physical cores over logical/virtual cores . For instance, if you compare a processor with two cores and hyper-threading with another with four physical cores, select the second one!
Moreover, hyperthreading is not necessary for most applications. Hyper-threading only adds value if you run multiple programs with high requirements simultaneously; even then, these programs must be able to utilize it.
Following the use case where CPU with Hyperthreading technology suits best:
Video encoding: If you are a professional, use high-quality software for 3D rendering or video encoding to create more threads, often involving heavy CPU usage. The additional logical threads provided by Hyper-threading can help speed up the encoding process.
Multitasking: Hyper-threading allows the CPU to handle multiple tasks concurrently by splitting each core into two threads. This is useful when performing tasks that require the use of multiple programs simultaneously, such as video editing or running multiple browser tabs.
Server workloads: Hyper-threading can be particularly beneficial in server environments where multiple applications run simultaneously. It allows for better resource utilization and can help improve overall server performance.
Gaming: While not all games use Hyper-threading, some newer titles can benefit from it. Games that utilize multi-threaded rendering or physics engines can perform better on CPUs with Hyper-threading enabled.
However, for regular use like word processing or web browsing, Hyperthreading is unlikely to speed up the harddisk or CPU performance for these basic computing tasks.
Also, in some cases, enabling Hyperthreading can hurt gaming performance due to increased latency and lower clock speeds, so check compatibility to CPU bottleneck for your gaming program before going with Hyperthreading.
Summary
- Hyperthreading divides each physical core of the CPU into two virtual cores.
- The physical core of the CPU is more powerful than the virtual one.
- Hyperthreading is important for high-performance software but not so important for simple programs.
- Related: How to Know will CPU be Compatible with my Motherboard?
- Also Read: Intel UHD Graphics vs Intel Iris Xe (New Series)
Now you know what to pay attention when buying a CPU. Just, ask yourself the question – how many programs that you will use with hyper-threading or SMT? If the answer is unclear, it is better to pay attention to other processor characteristics, such as the number of cores, frequency, amount of L3 cache.
Что такое Hyper-Threading

What type of information is stored in a log file?
- 12/14/2022
- Web analytics
Log files contain a range of information on system processes, programs, and services. Whether it’s an operating system, database, or antivirus software: all of this information on relevant processes is stored in each respective log file. This enables extensive data recovery and allows users to find a quick solution when faced with troubleshooting tasks; it also helps with software adjustments.…

How to update BIOS
- 01/05/2023
- Configuration
Have you recently bought and installed a new processor, but your computer is still not working? You might have to update your BIOS or (U)EFI first. The software ensures that all the important components are available when booting the system. But it’s not as simple as upgrading to update the BIOS. What steps do you need to take to update the BIOS?

What is Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA)?
- 01/28/2021
- Know-how
Remote direct memory access technology makes it possible to transfer data at maximum speed, very low latency and without burdening the CPU. The RDMA transfer process does not utilize a computer’s processor nor its operating system, which results in a data transfer that is considerably quicker. Find out how it works in this article.
Что такое Hyper-Threading
Будь в курсе последних новостей из мира гаджетов и технологий
iGuides для смартфонов Apple

Технология Intel Hyper-Threading — что это и как работает

Егор Морозов — 31 января 2017, 16:50

Впервые технология Hyper-Threading (HT, гиперпоточность) появилась 15 лет назад — в 2002 году, в процессорах Pentium 4 и Xeon, и с тех пор то появлялась в процессорах Intel (в линейке Core i, некоторых Atom, в последнее время еще и в Pentium), то исчезала (ее поддержки не было в линейках Core 2 Duo и Quad). И за это время она обросла мифическими свойствами — дескать ее наличие чуть ли не удваивает производительность процессора, превращая слабые i3 в мощные i5. При этом другие говорят что HT — обычная маркетинговая уловка, и толку от нее мало. Правда как обычно по середине — местами толк от нее есть, но двухкртаного прироста ждать точно не стоит.
Техническое описание технологии
Начнем с определения, данного на сайте Intel:
-
может хранить информацию сразу о нескольких выполняющихся потоках;
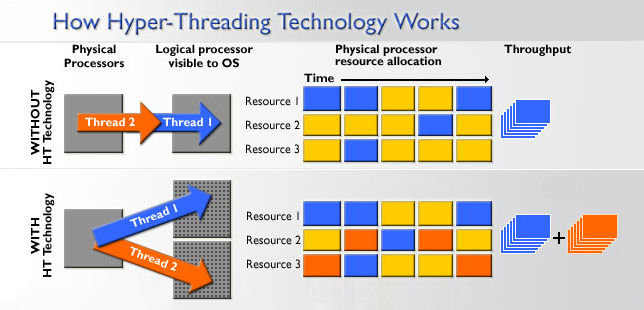
Допустим перед процессором стоят две задачи. Если процессор имеет одно ядро, то он будет выполнять их последовательно, если два — то параллельно на двух ядрах, и время выполнения обеих задач будет равно времени, затраченному на более тяжелую задачу. Но что если процессор одноядерный, но поддерживает гиперпоточность? Как видно на картинке выше при выполнении одной задачи процессор не занят на 100% — какие-то блоки процессора банально не нужны в данной задаче, где-то ошибается модуль предсказания переходов (который нужен для предсказания, будет ли выполнен условный переход в программе), где-то происходит ошибка обращения к кэшу — в общем и целом при выполнении задачи процессор редко бывает занят больше, чем на 70%. А технология HT как раз «подпихивает» незанятым блокам процессора вторую задачу, и получается что одновременно на одном ядре обрабатываются две задачи. Однако удвоения производительности не происходит по понятным причинам — очень часто получается так, что двум задачам нужен один и тот же вычислительный блок в процессоре, и тогда мы видим простой: пока одна задача обрабатывается, выполнение второй на это время просто останавливается (синие квадраты — первая задача, зеленые — вторая, красные — обращение задач к одному и тому же блоку в процессоре):
В итоге время, затраченное процессором с HT на две задачи, оказывается больше времени, требуемого на вычисление самой тяжелой задачи, но меньше того времени, которое нужно для последовательного вычисления обеих задач.
Плюсы и минусы технологии
С учетом того, что кристалл процессора с поддержкой HT физчески больше кристалла процессора без HT в среднем на 5% (именно столько занимают дополнительные блоки регистров и контроллеры прерываний), а поддержка HT позволяет нагрузить процессор на 90-95%, то в сравнении с 70% без HT мы получаем, что прирост в лучшем случае будет 20-30% — цифра достаточно большая.
-
Нехватка кэш-памяти. К примеру в современных четырехядерных i5 находится 6 мб кэша L3 — по 1.5 мб на ядро. В четырехядерных i7 с HT кэша уже 8 мб, но так как логических ядер 8, то мы получаем уже только 1 мб на ядро — при вычислениях некоторым программам этого объема может не хватать, что приводит к падению производительности.
Программы, плохо работающие с гиперпоточностью
Традиционно это большинство игр — их обычно бывает трудно грамотно распараллелить, поэтому зачастую четырех физических ядер на высоких частотах (i5 K-серии) более чем хватает для игр, распараллелить которые под 8 логических ядер в i7 оказывается непосильной задачей. Однако стоит учитывать и то, что есть фоновые процессы, и если процессор не поддерживает HT, то их обработка ложится на физические ядра, что может замедлить игру. Тут i7 с HT оказывается в выигрыше — все фоновые задачи традиционно имеют пониженный приоритет, поэтому при одновременной работе на одном физическом ядре игры и фоновой задаче игра будет получать повышенный приоритет, и при этом фоновая задача не будет «отвлекать» занятые игрой ядра — именно поэтому для стриминга или записи игр лучше брать i7 с гиперпоточностью.
Итоги
Пожалуй тут остается только один вопрос — так имеет ли смысл брать процессоры с HT или нет? Если вы любите держать одновременно открытыми пяток программ и при этом играть в игры, или же занимаетесь обработкой фото, видео или моделированием — да, разумеется стоит брать. А если вы привыкли перед запуском тяжелой программы закрывать все другие, и не балуетесь обработкой или моделированием, то процессор с HT вам ни к чему.
При подготовке материала использовались источники:
https://computermesh.com/what-is-hyper-threading-how-does-it-work/
https://www.ionos.com/digitalguide/server/know-how/hyperthreading/
https://www.iguides.ru/main/gadgets/other_vendors/tekhnologiya_intel_hyper_threading_chto_eto_i_kak_rabotaet/